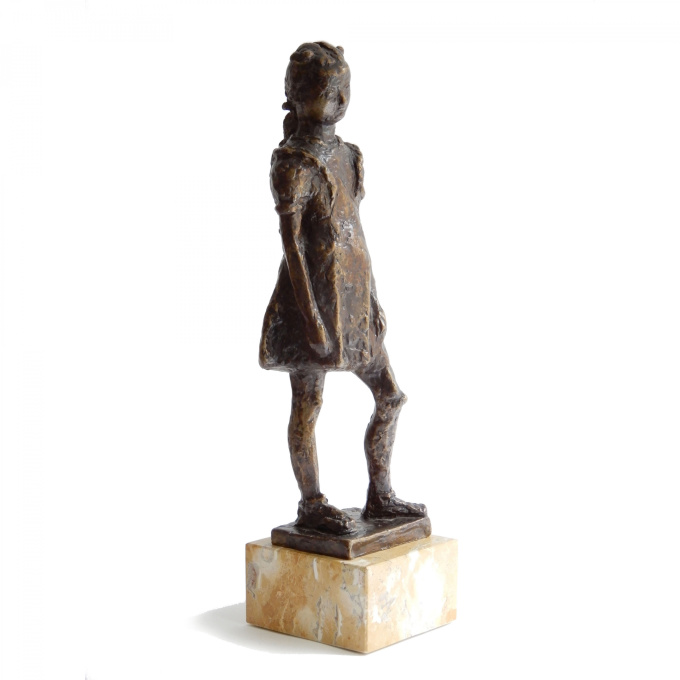
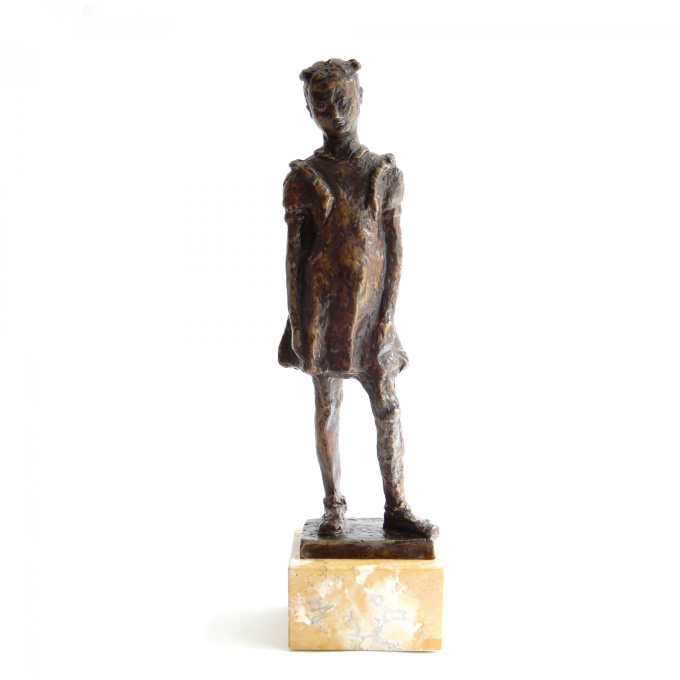
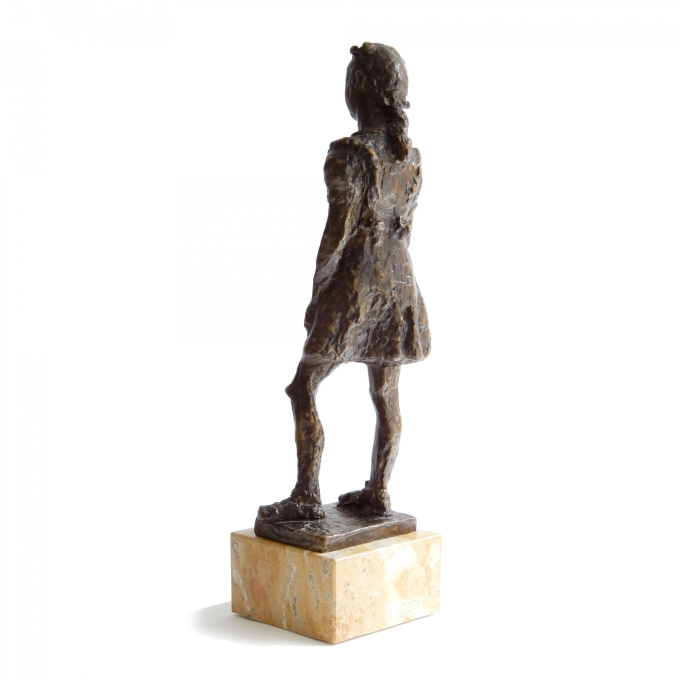
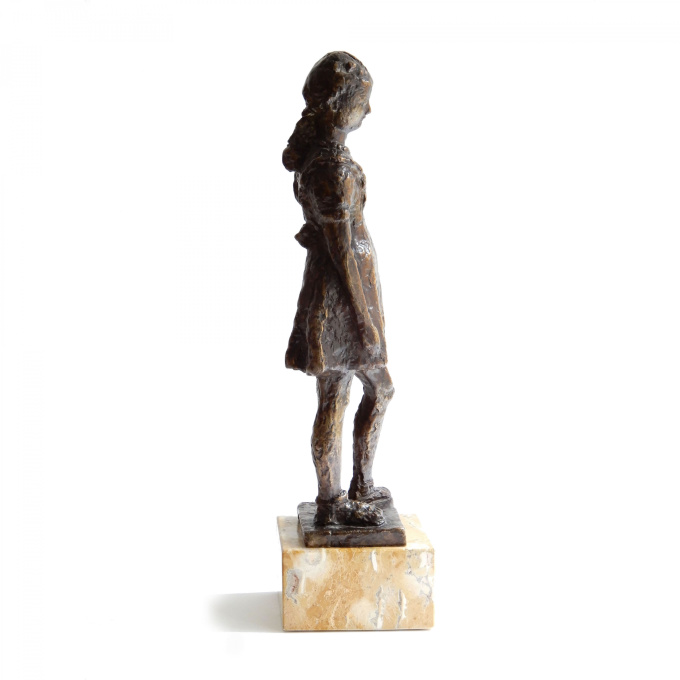
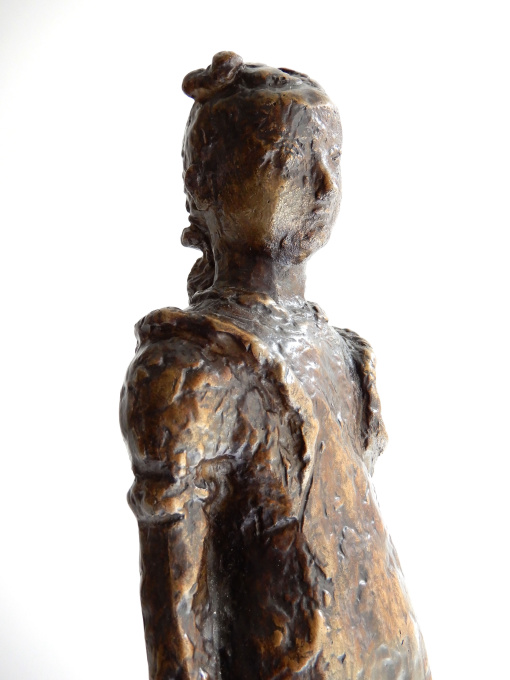
Fillette à robe à volant 1948
Léon Indenbaum
BronzeMetall
50 ⨯ 13 ⨯ 11 cm
ConditionExcellent
Preis auf Anfrage
Dille Art
- Über KunstwerkThere's something touching about this girl in her prettiest ruffled dress with a bow in her hair. Indenbaum made this sculpture of plaster in 1948. So far, 7 of the 8 copies have been cast in bronze. This is number 7/8.
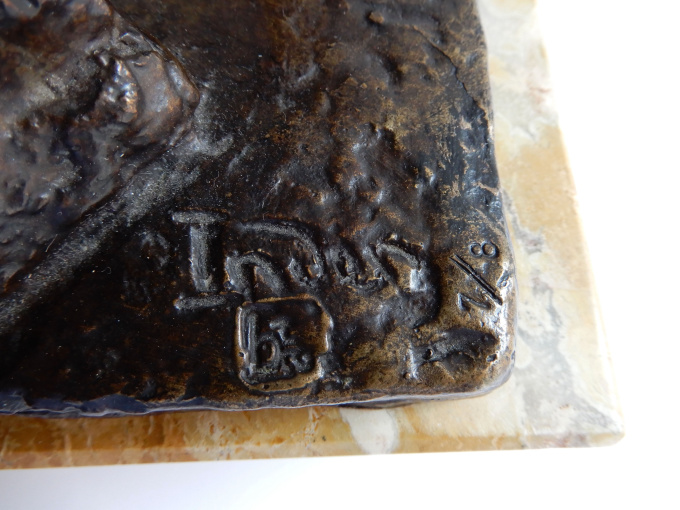
It stands on a beautiful marble pedestal and is extensively signed with "Inden, 7/8" and the hallmark of the bronze founder Barthélemy.
----
The family had this sculpture cast in bronze posthumously, because the family believes that their grandfather's sculptures should be seen, they want to give the name Indenbaum the attention and fame it deserves. Léon Indenbaum is known to connoisseurs and is inextricably linked to the Ecole de Paris. Yet they only want to sell a few works, to a very limited extent.
These posthumous sculptures are therefore a first and also the last edition of a maximum of 12. Each sculpture is numbered and officially registered, maximum 8 are numbered 1-8 and four of them are signed EA I to EA IV. (EA stands for Epreuve d'Artiste). This is number 3/8. More examples will not be cast either.
This sculpture also includes an official certificate signed by Léon Indenbaum's grandson. This sculpture with certificate is also registered with ADAGP (Société des authors dans les arts graphiques et plastiques) in Paris.
Biography:
Leon Indenbaum (Tcherikov, now Belarus, 1890 - Opio, 1981), was a Russian/French sculptor who belonged to the group of artists of the École de Paris. His art was innovative, inspired by the classics, but also by African art, the Cubism and Expressionism.
Léon Indenbaum grew up in the shtetl (Eastern European Jewish village) Tcherikov, with his grandfather, who was a bookbinder of art books. After primary school, he was educated as a woodworker. The director of that school thought he was so talented that he arranged for him to attend the Academy of Decorative Arts in Vilnius.
After this training, Indenbaum wanted more and was admitted to the Imperial Academy in Odessa. He went through it for a few years until he crossed a wrong box on a form, he had accidentally signed for 5 years military service in the Imperial Army.
He already had contacts with an artist friend who was in Paris, where so much was happening in the field of art.
Indenbaum managed to escape from Vilnius with the help of an engineer and arrived in Paris in March 1911.
He ended up in 'La Ruche' in Montparnasse, a kind of artists' village.
La Ruche was a circular building, it served as a wine pavilion at the 1900 World's Fair, and was rebuilt by the successful artist Alfred Boucher. Boucher wanted to give poor artists a chance to devote themselves completely to their art. La Ruche was a large round building full of studio apartments, each room had the shape of a slice of pie, in the point a space for a kitchen and storage and above the door was a small loft where you could sleep, often such a studio also had to be shared.
Indenbaum got a studio on the 2nd floor, next to Chagall, who, like himself, had also just arrived from Russia. Indenbaum lived in La Ruche until 1927.
He did have a second studio in Montparnasse for a while.
In total, about 200 artists lived in La Ruche, many of them were from Eastern Europe and many of them were Jewish. Some of them have become world famous with their art, think of Chaïm Soutine, Ossip Zadkine, Jacques Lipschitz, Chana Orloff, Michael Kikoïne, Moïse Kisling , Amadeo Modigliani to name a few.
From 1911 to 1919, Indenbaum studied
sculpture at the Académie La Grande Chaumière, his mentor was the sculptor and painter Antoine Bourdelle, first as a student, later also as his assistant.
In 1912 Indenbaum already exhibited at the Paris Salon d'Artistes Indépendents, he was very poor and his choice of materials was cheap. Jacques Doucet, the great art collector and famous couturier, saw a bust of Indenbaum and summoned him to his home, he wanted the same bust made in a different material, Indenbaum managed to get a piece of onyx.
Doucet was very pleased and asked Indenbaum to make a relief for his round dining room. Indenbaum received 1000 francs per month. Indenbaum had found his patron.
He made one of his most impressive reliefs, entitled 'Musiciens et antelopes' from 1914, made of pink onyx. It was auctioned at Christie's in 2004 for 3.3 million euros.
Besides Jacques Doucet, the couturier René Poiret, the bankers George and Marcel Bénard and the decorator, designer and collector Marcel Coard were regular customers of Léon Indenbaum's sculptures and reliefs.
Léon fell in love with Céline Hénin, she became his muse and his wife, at the end of 1914 they had a daughter, Dinah. Indenbaum was doing well. He had many friends, such as the artists Chaim Soutine, Amadeo Modigliani, with whom he also shared a studio for a period, Tsuguharu Foujita, Chana Orloff, Michael Kikoïne, and Diego Rivera.
Amadeo Modigliani and Diego Rivera both portrayed Indenbaum in 1913 and 1916. Indenbaum himself also portrayed several of his friends. It was the happiest period of his life.
With the stock market crash of 1929, life became much more difficult, people lost their fortunes and could no longer afford works of art. The political situation in France also changed.
The artists from La Ruche and Montparnasse were mostly migrants, at the Paris Salon they were not allowed to exhibit their work among the French artists, an art critic, André Warnod, had given them the nickname 'École de Paris', to show that this innovative avant-garde garde art was also French art. In the 1930s this name was used derogatorily, they were looked down upon, their art was called depraved and because many of them were Jewish, there was also anti-Semitism. They were ignored in the press and in the late 1930s they were no longer allowed to exhibit.
Some artists went abroad. When the war broke out, many had to flee or go into hiding. Indenbaum also had to leave Paris in a hurry. He found a hiding place in a village in the Seine et Marne, where he always got his clay. He was lucky and survived the war, more than 60 percent of the Jewish artists in La Ruche died in the camps.
After the war, Indenbaum settled in Paris again. His studio had been looted and what was left was sometimes destroyed. He lived a very withdrawn life. He had already been separated from Céline before the war, his daughter lived in the south of France. His friends had either not survived the war or had become much too commercial in his view.
He never wanted to commit to a gallery, he felt that he sold his soul, his independence as an artist was at stake, the result was that he was ignored by a large part of the art world. His now famous friends had signed and they were doing well.
Indenbaum wanted nothing more than to work in complete freedom, but in doing so he made it very difficult for him self. He also refused, for example, major commissions from the French state for work on monuments and facades of special buildings.
He was, however, one of the founders of the "Groupe des neuf", a group of nine sculptors who gathered on November 11, 1963 at the statue of Balzac on Avenue Raspail, made by Auguste Rodin.
It was a tribute. They wanted to create a monument to French post-war figurative sculpture at a time when American art was beginning to take over.
The 'Groupe des neuf' consisted of Jean Carton, Paul Cornet, Raymond Corbin, Marcel Damboise, Léon Indembaum, Léopold Kretz, Raymond Martin, Gunnar Nilsson and Jean Osouf. It was a success, there were several exhibitions ofthe group, including in Musée Rodin, a total of 22 sculptors joined the group.
In 1968 Indenbaum received the prestigious Prix de sculpture Georges Wildenstein, from the Institut de France, for his entire oeuvre. In the same year he decided to move to his daughter in Opio. He died at the age of 91. A long life entirely devoted to creating art.
Léon Indenbaum's work can be seen in various museums, including in the United States, Switzerland, Russia, Belarus, Israel and of course in France. Sometimes his work is also auctioned at the major auction houses such as Christies, Sotheby's and MacDougall in London.
Dille Art is the only gallery that represents Léon Indenbaum's sculptures in collaboration with the family of Indenbaum.
Literature and sources:
- Family of Indenbaum
- Jeanine Warnod; "Les artistes de Montparnasse, la Ruche", Éditions Mayer-Van Wilder, Paris 1988. P.42-47, 8, 87,96, 104, 159, 162, 170, 192.
- Nieszawer & Princ; "Histoires des artistes Juifs de l'École de Paris, 1905-1939", Édition Les Étoiles, 2020. P. 190-192, 515 and 516.
- Jeanine Warnod; "l'École de Paris", Édition Musée du Montparnasse, 2012. P. 239, 240 and 243.
- "Chagall, Modigliani, Soutine.... Paris pour école, 1905-1940", Éditions Musée d'Art et d'Histoire du Judaïsme (MAHJ), Paris, 2020 et Réunion des Musée nationaux, Grand Palais, 2020. P. 8, 11, 49, 66, 68, 69, 228, 230, 252.
- G. Annenkoff; "Art Russe Moderne", Éditions Laville, Paris, 1928. P. 50 and 51. - Über Künstler
Léon Indenbaum (Tcherikov, heute Weißrussland, 1890 - Opio, 1981) war ein russisch-französischer Bildhauer, der zur Künstlergruppe der cole de Paris gehörte. Seine Kunst war innovativ, inspiriert von den Klassikern, aber auch von afrikanischer Kunst, Kubismus und Expressionismus.
Indenbaum wuchs im Schtetl (osteuropäisches jüdisches Dorf) Tcherikov bei seinem Großvater auf, der Kunstbuchbuchbinder war. Nach der Grundschule machte er eine Ausbildung zum Holzarbeiter. Der Direktor dieser Schule hielt ihn für so talentiert, dass er ihm den Besuch der Kunstgewerbeakademie in Vilnius arrangierte.
Nach dieser Ausbildung wollte Indenbaum mehr und wurde an der Kaiserlichen Akademie in Odessa aufgenommen. Er ging einige Jahre durch, bis er auf einem Formular ein falsches Kästchen angekreuzt hatte, er hatte versehentlich 5 Jahre Militärdienst in der kaiserlichen Armee unterschrieben. Er hatte bereits Kontakte zu einem befreundeten Künstler, der in Paris war, wo im Bereich der Kunst so viel passierte. Indenbaum gelang mit Hilfe eines Ingenieurs die Flucht aus Vilnius und kam im März 1911 in Paris an.
Er landete in „La Ruche“ in Montparnasse, einer Art Künstlerdorf. La Ruche war ein Rundbau, diente als Weinpavillon auf der Weltausstellung 1900 und wurde vom erfolgreichen Künstler Alfred Boucher wieder aufgebaut. Boucher wollte armen Künstlern eine Chance geben, sich ganz ihrer Kunst zu widmen. La Ruche war ein großes rundes Gebäude voller Studio-Apartments, jedes Zimmer hatte die Form eines Kuchenstücks, im Wesentlichen Platz für eine Küche und Lager und über der Tür war ein kleiner Schlafboden, oft so ein Studio musste auch noch geteilt werden.
Indenbaum bekam im 2. Stock ein Atelier neben Chagall, der wie er auch gerade aus Russland eingereist war. Indenbaum lebte bis 1927 in La Ruche. Er hatte zeitweise ein zweites Atelier in Montparnasse.
Insgesamt lebten in La Ruche etwa 200 Künstler, viele von ihnen kamen aus Osteuropa und viele von ihnen waren Juden. Einige von ihnen sind mit ihrer Kunst weltberühmt geworden, denken Sie an Chaïm Soutine, Ossip Zadkine, Jacques Lipschitz, Chana Orloff, Michael Kikoïne, Moïse Kisling, Amadeo Modigliani, um nur einige zu nennen.
Von 1911 bis 1919 studierte Indenbaum Bildhauerei an der Académie La Grande Chaumière bei dem Bildhauer und Maler Antoine Bourdelle, zunächst als Student, später auch als dessen Assistent.
1912 stellte Indenbaum bereits auf dem Pariser Salon d'Artistes Indépendents aus, er war sehr arm und die Materialwahl war billig. Jacques Doucet, der große Kunstsammler und berühmte Modeschöpfer, sah eine Büste von Indenbaum und rief ihn zu sich nach Hause, er wollte dieselbe Büste aus einem anderen Material, Indenbaum schaffte es, ein Stück Onyx zu bekommen. Doucet war sehr erfreut und bat Indenbaum, eine Erleichterung für sein rundes Esszimmer zu machen. Indenbaum erhielt monatlich 1000 Franken. Indenbaum hatte seinen Gönner gefunden. Eines seiner beeindruckendsten Reliefs mit dem Titel „Musiciens et antilopes“ aus dem Jahr 1914 fertigte er aus rosa Onyx an. Es wurde 2004 bei Christie's für 3,3 Millionen Euro versteigert.
Além de Jacques Doucet, o costureiro René Poiret, os banqueiros George e Marcel Bénard e o decorador, designer e colecionador Marcel Coard eram clientes regulares das esculturas e relevos de Léon Indenbaum.
Léon se apaixonou por Céline Hénin, ela se tornou sua musa e sua esposa, no final de 1914 eles tiveram uma filha, Dinah. Indenbaum estava indo bem. Teve muitos amigos, como os artistas Chaim Soutine, Amadeo Modigliani, com quem também dividiu um estúdio por um período, Tsuguharu Foujita, Chana Orloff, Michael Kikoïne e Diego Rivera.
Amadeo Modigliani e Diego Rivera retrataram Indenbaum em 1913 e 1916. O próprio Indenbaum também retratou vários de seus amigos. Foi o período mais feliz de sua vida.
Com a quebra da bolsa de valores em 1929, a vida tornou-se muito mais difícil, as pessoas perderam suas fortunas e não podiam mais comprar obras de arte. A situação política na França também mudou. Os artistas de La Ruche e Montparnasse eram na sua maioria migrantes, no Salão de Paris não podiam conviver com os artistas franceses, um crítico de arte, André Warnod, deu-lhes o apelido de 'École de Paris', para mostrar que este inovador a arte de vanguarda também era arte francesa. Na década de 1930 esse nome era usado depreciativamente, eles eram desprezados, sua arte era chamada de depravada e, como muitos deles eram judeus, havia também o anti-semitismo. Eles foram ignorados pela imprensa e no final da década de 1930 não tinham mais permissão para expor. Alguns artistas foram para o exterior. Quando a guerra estourou, muitos tiveram que fugir ou se esconder. Indenbaum também teve que deixar Paris às pressas. Ele encontrou um esconderijo em uma vila no Seine et Marne, onde sempre pegava sua argila. Ele teve sorte e sobreviveu à guerra, mais de 60 por cento dos artistas judeus em La Ruche morreram nos campos.
Após a guerra, Indenbaum estabeleceu-se novamente em Paris. Seu estúdio havia sido saqueado e o que restava às vezes era destruído. Ele viveu muito retraído. Ele já havia se separado da Céline antes da guerra, sua filha morava no sul da França. Seus amigos não sobreviveram à guerra ou se tornaram muito comerciais em sua opinião.
Ele nunca quis se comprometer com uma galeria, sentiu que vendeu sua alma, sua independência como artista estava em jogo, o resultado foi que ele foi ignorado por grande parte do mundo da arte. Seus amigos, agora famosos, haviam assinado e estavam indo bem. Indenbaum não queria nada mais do que trabalhar em completa liberdade, mas, ao fazê-lo, jogou seus próprios óculos. Ele também recusou, por exemplo, grandes encomendas do Estado francês para obras em monumentos e fachadas de edifícios especiais.
Em 1968 Indenbaum recebeu o prestigioso Prix de sculpture Georges Wildenstein, do Institut de France, por todo o seu trabalho. Nos últimos anos, ele morou com sua filha em Opio. Ele morreu com 91 anos. Uma longa vida inteiramente dedicada à criação de arte.
O trabalho de Léon Indenbaum pode ser visto em vários museus, incluindo nos Estados Unidos, Suíça, Rússia, Bielo-Rússia, Israel e, claro, na França. Às vezes, seu trabalho também é leiloado nas principais casas de leilão como Christies, Sotheby's e MacDougall em Londres.
Sind Sie daran interessiert, dieses Kunstwerk zu kaufen?
Artwork details
Related artworks
- 1 - 4 / 5
Willem van Konijnenburg
Landscape in Limburg, the south of the Netherlands1868 - 1943
Preis auf AnfrageKunsthandel Pygmalion
1 - 4 / 24Arie Teeuwisse
Titania and Nick Bottom (the weaver)20th century
Preis auf AnfrageKunsthandel Pygmalion
1 - 4 / 24Mary Alacoque Waters
'Unknown Twins' after Rafael1999 - 2004
Preis auf AnfrageGalerie Mia Joosten Amsterdam
1 - 4 / 24- 1 - 4 / 24
- 1 - 4 / 12